Biological Membranes Contain Bilayers of Which of the Following Lipis
I NPlipid head contact with the release of citrate in the water phase ligand exchange. Start studying Exercise 6-1 Standard Plate Count.
Cc What Is The Phospholipid Bilayer And What Determines Its Fluidity
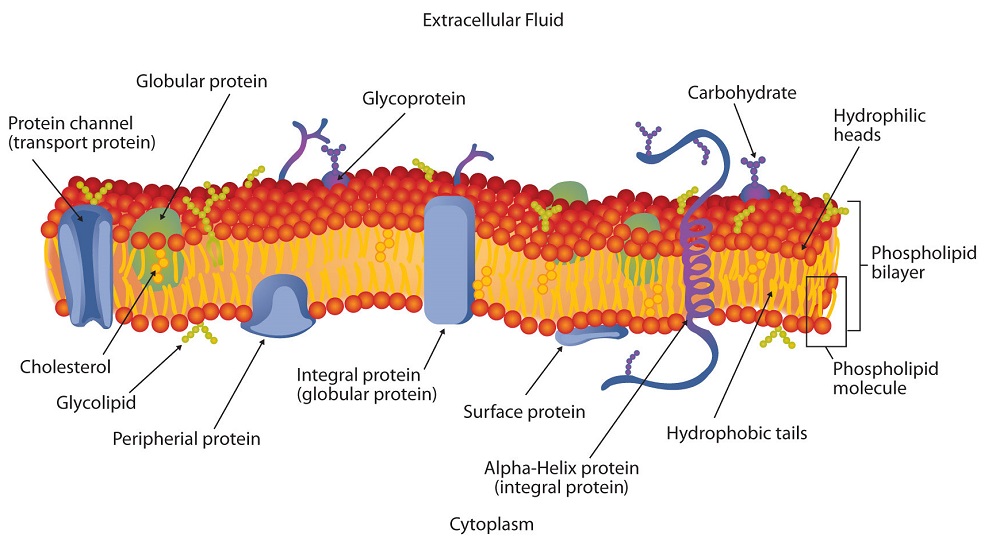
As complex mixtures of lipids proteins and sugars biological membranes serve vital functions such as providing shape and structure mediating signaling recognition selective permeation etc.

. Ii headtail flipping of the lipid in contact with the NP. Membrane lipids are amphipathic. The cell membrane is made of the lipid bilayer which contains lipids and proteins.
Composition of the lipid bilayer. Lab 2- Exercise 4. The three major classes of membrane lipids are phospholipids glycolipids and cholesterol.
Are the metabolic machinery of the cell and that are highly organized to carry out specific functions for the cell as a whole. There are three major membrane lipids. Measurement of ionic conductance changes through ion channels requires a robust biological.
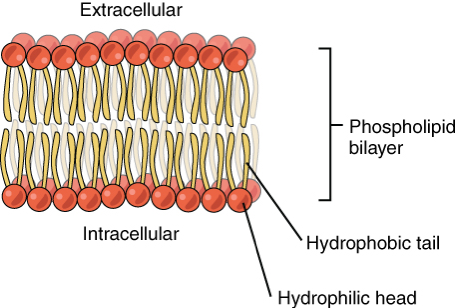
In aqueous mediums membrane lipids spontaneously organize into bilayers with the polar ends oriented towards and the non-polar ends oriented away from the solution. The membranes of biological cells are complex structures consisting primarily of lipids but also contain cholesterol carbohydrates proteins and other complex macromolecules. Membrane lipids are a group of compounds which form the double-layered surface of all cells.
A functional environment for ion channels. The first part of the book focuses on the fundamentals of lipid bilayers and membrane proteins. Our present picture of cell membranes as lipid bilayers is the legacy of a centurys study that concentrated on the lipids and proteins of cell-surface membranes.
These basic structural properties of plasma membranes enable them to carry out their fundamental functions. They have one end that is soluble in water and an ending that is soluble in fat. The compounds in biological membranes that form a barrier to the movement of materials across the membrane.
Each lipid membrane contains 2 molar concentration of spin probes corresponding to 12 spin probe molecules in a bilayer 6 spin probe molecules per leaflet. From Basic Research to Application describes state-of-the-art research and future directions in the field of membranes. Define the following term.
The structural and functional unit of all living things is a complete entity. About this Research Topic. Most biological membranes contain a variety of lipids including the various glycerophospholipids such as phosphatidyl-choline -ethanolamine -serine -inositol and -glycerol as well as sphingomyelin and in some membranes glycosphingolipids.
1 glycerophospholipids in which the hydrophobic regions are. 17_____ Which membrane lipid contains an amide bond. Bilayer lipid membranes supported on Teflon filters.
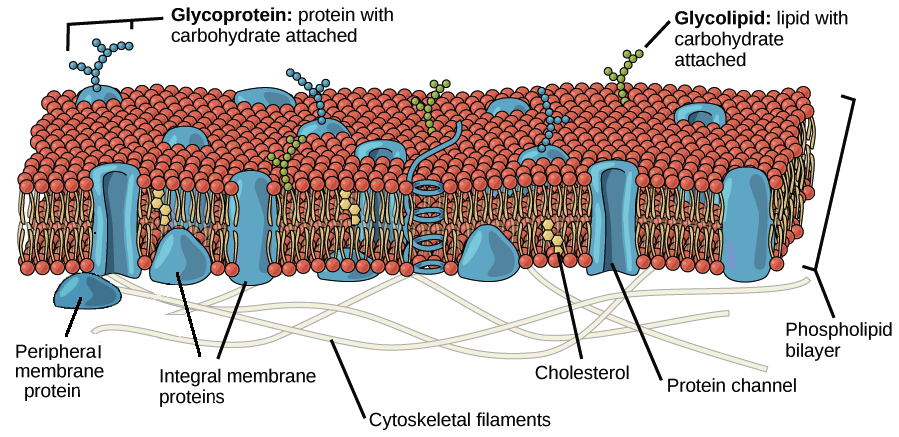
The bilayer closes in on itself to avoid free edges with water. The membrane asymmetry in lipid and protein composition led to the proposal of the bilayer couple hypothesis. The carbohydrates of membranes are attached either to lipid forming glycolipids of various classes or to proteins forming glycoproteins.
Composition and Structure of Biological Membranes. Their hydrophobic interactions with each other and their hydrophilic interactions with water direct their packing into sheets called membrane bilayers. Lies closest to the dermis and is connected to it along a wavy borderline receives some nutrients from the.
This states that the two monolayers of the membrane bilayer may respond differently to various forces while remaining coupled to each other. Up to 8 cash back As a result of their unique physical properties biological membrane mimetics such as liposomes are used in a broad range of scientific and technological applications. Liposomes Lipid Bilayers and Model Membranes.
D Membranes contain lipids that polymerize into one large molecule. Details of the preparation of the lipid bilayer systems contacting. Made of 5 layers stratified squamous epithelium that is hard and rough avascular cells constantly dividing.
The lipid bilayer or phospholipid bilayer is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid moleculesThese membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cellsThe cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses are made of a lipid bilayer as are the nuclear membrane surrounding the cell nucleus and membranes of the membrane-bound. The cell and most organelles are covered by membranes separating the inside from the outside. Homochiral membrane bilayers organize biological functions in all domains of life.
Up to 8 cash back The Structure of Biological Membranes Third Edition provides readers with an understanding of membrane structure and function that is rooted in the history of the field and brought to the forefront of current knowledge. Due to their high content of sphingomyelin SM and cholesterol raft bilayers are thicker than nonraft bilayers and at least at 4C are resistant to Triton X-100 extraction. Amphipathic lipids which have polar and non-polar.
This hypothesis is the basis for the possible shape changes observed in membranes. All biological membranes contain lipids that prefer to adopt a non-bilayer phase. Which is a characteristic of biological membranes.
B Membranes have an asymmetrical micelle structure. By forming a double layer with the polar ends pointing outwards and the nonpolar ends. Define the following term.
C Membranes have hydrophobic groups on the surfaces. Specific proteins and lipids sequester to regions of cell membranes called rafts. The membranes permeabilityits key propertycorrelates with.
Many ion channel proteins have binding sites for toxins and pharmaceutical drugs and therefore have much promise as the sensing entity in high throughput technologies and biosensor devices. Recent results suggest that in the thylakoid membrane membrane proteins force all the lipids to adopt a bilayer structure and that the non-bilayer-forming lipids in the thylakoid membrane serve to drive the formation of membrane stacks. One end of the molecule is hydrophobic the other hydrophilic.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. In an effort to better understand biological membranes researchers often study artificially self-assembled vesicles or planar membranes. DPPC membranes contained 488 lipids and DPPCCHOL mixtures with 408 and 180 molecules of DPPC and CHOL respectively.
And iii the formation of a complete lipid bilayer around. The lipid and protein compositions of membranes vary from cell type to cell. As indicated above biological membranes are composed of lipids proteins and carbohydrates.
Similarly to what was described for POPC membranes the membrane wrapped the NP over the following stages top row of Figure 2. A Membranes contain proteins and amphipathic lipids. Recent work is changing.
17 3 Membranes And Membrane Lipids Chemistry Libretexts
No comments for "Biological Membranes Contain Bilayers of Which of the Following Lipis"
Post a Comment